Quickstart Guide: Using Scuba's API to Expand on UI Queries [v5]
The Scuba external API lets you extract summarized and aggregated data for use in downstream processes, dashboards, or reports.
To use the API, you need the following:
An API token
A query response identifier (you can also use a BQL query, but this guide will assume you are building your query in the UI first)
Once you have these two pieces of information, you can submit POST requests through the API.
API queries use cluster resources on a scale similar to ad hoc queries initiated in the Scuba UI. To maintain performance across your Scuba cluster when using the query API, use the same best practices for query efficiency that you use with queries that originate in the UI.
Step 1: Generate an API token
You can generate an API token using your browser:
In your browser, log into Scuba.
In the URL bar, append
/api/create_tokento the host name of your Scuba cluster and hit Enter. For example, if your Scuba host name is https://my_cluster.scuba.io, enter https://my_cluster.scuba.io/api/create_token.The browser immediately returns either a failure message or a success message with an API token. A success message looks like this:
CODE{"token": "san+aslnasw50293sjlfhgnoOvWW/sQH09y0", "success": true}The quoted string after "token" is the token (without the quotes). Copy (and paste) the token to use later.
Step 2: Create a query
You have two ways to create a query. This guide assumes you are defining queries in Scuba’s UI and using the API to expand on those results.
Define a query in the UI
Use the UI to define the query you wish to make programmatic. Press RUN to run the query.
The URL in your browser will append a queryResponseId, like
r9372, to the cluster URL. Copy this identifier to use in the API later.
Once you've defined your query and have the queryResponseId, proceed to the next step.
Step 3: Use the API in Postman
Reference: Postman Tutorial: How to use Postman Tool for API Testing (guru99.com)
Set up a Postman account (or log into your existing account)
Postman is a scalable, open-source API testing tool. More information on how to use Postman can be found in their docs here, or you can simply use this guide.
You will need to create a Postman account, which can either be password-based, or linked to your Google account. Go to https://identity.getpostman.com/ to create, or access, your account. Once you have set up your account, we also recommend bookmarking your Postman homepage for easier future access.
Create an API request
The API accepts HTTP POST requests from any HTTP client (for example, curl or a UI-based HTTP client).
| Query response ID | BQL query |
Endpoint |
|
|
Request parameter format | JSON in the body of the request in the | JSON in the body of the request in the |
Example request body |
|
|
In your preferred workspace, click the New button and select the HTTP option. Once the request is open, change the GET drop-down to say POST, then enter the URL at which you access the Scuba UI into the field to the right:
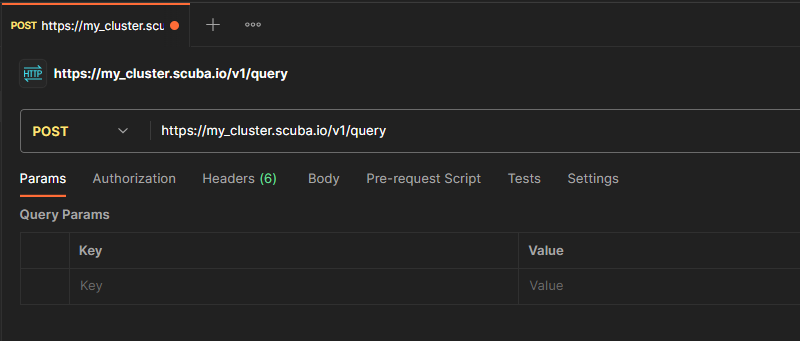
Remember to change “my_cluster.scuba.io” with your cluster URL.
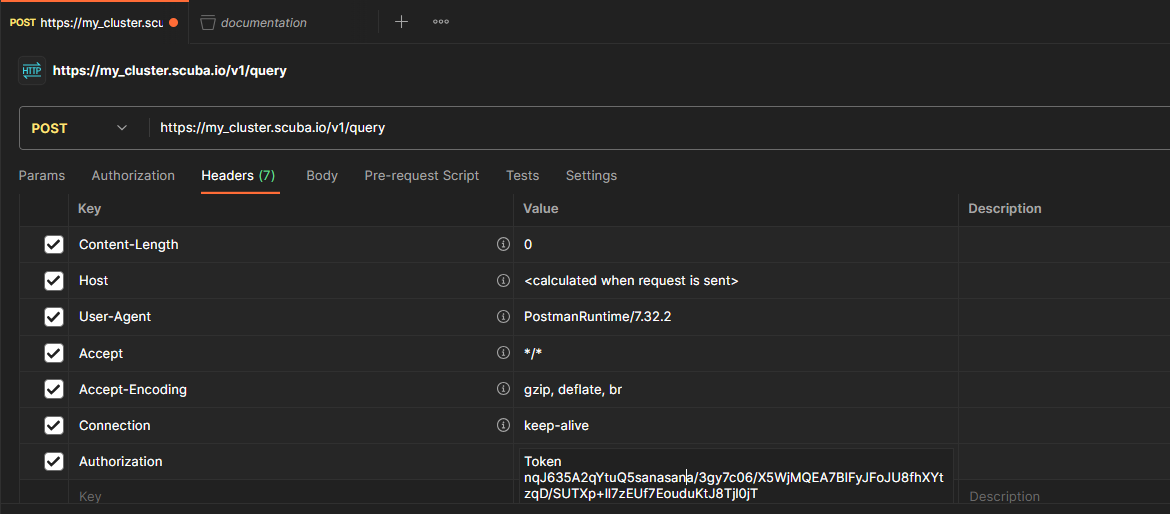
Then, under the “Headers” tab, type Authorization in the “Key” field; enter Token and your API token, separated by a single space, into the “Value” field:
Now you’re ready to input your query request! Once you’ve created your query in the UI, copy the /r##### value from the URL and enter it into the “Body” tab. You’ll need to change the type to raw and format to JSON. Here's an example of what that looks like:
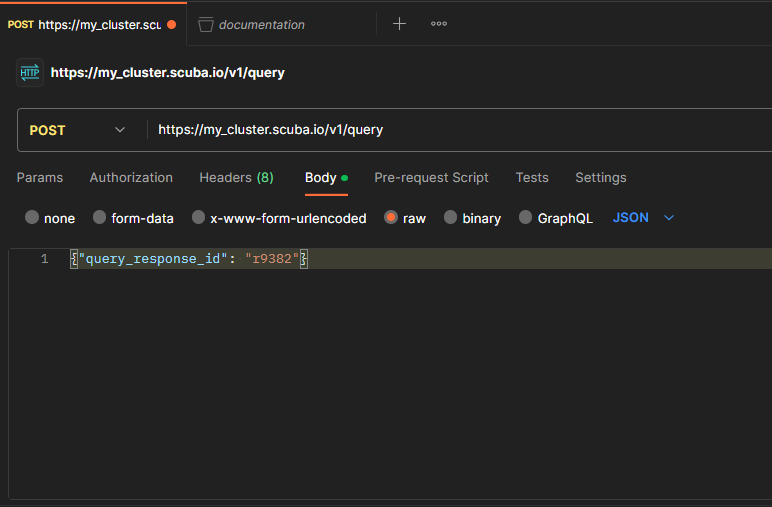
Click the Send button to send your API request. By default, the API will return a JSON-formatted output; see Use the Scuba external query API for information on returning a cluster URL and other request options.
Sample requests via other API clients
If you are using curl to make your requests, you can optionally use the --verbose flag and receive some output below the request, before the curl response. In this case, the request and confirmation output is as follows:
$ curl 'https://my_cluster.scuba.io/v1/query' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'Authorization: Token san+aslnasw50293sjlfhgnoOvWW/sQH09y0' \
-d '{"query_response_id": "r9372"}' --verbose
> POST /v1/query HTTP/2
> Host: my_cluster.scuba.io
> User-Agent: curl/7.54.0
> Accept: */*
> Content-type: application/json
> Authorization: Token san+aslnasw50293sjlfhgnoOvWW/sQH09y0
> Content-Length: 32
Pass the API token in the Authorization header prefixed with "Token" and separated by a single space.
If instead of curl, you are using an HTTP client, the POST request might look like the following:
POST /v1/query
HTTP/2
Host: my_cluster.scuba.io
Authorization: Token san+aslnasw50293sjlfhgnoOvWW/sQH09y0
Content-Type: application/json {"query_response_id": "r9372"}Response
The response includes:
start and end times for every measurement
a measurement value for each defined measure
a value for any split-bys
Here is a sample response for a simple show count of events query splitting by artist:
[
{
"measure 1":473,
"end_time_0":1540846400000,
"start_time_0":1540760000000
"artist": "All Others"
},
{
"measure 1": 130,
"end_time_0": 1540364400000,
"start_time_0": 1509260400000,
"artist": "Gorillaz"
},
{ "measure 1": 11,
"end_time_0": 154103400000,
"start_time_0": 15124300000,
"artist": "Beethoven"
},
...
]